The human ear can detect sound waves as low as 20 Hz and as high as 20,000 Hz!
The inner ear is also called the “labyrinth” and is responsible for balance as well as sound detection. Researchers believe that fish have an inner ear similar to ours, which helps them detect water currents.
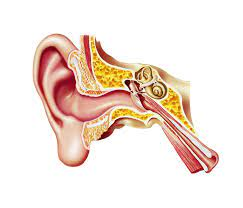
The ear canals themselves are self-cleaning. Earwax acts as the body’s own defence system because it is antifungal and antibacterial, and keeps dirt and debris out of the ear canal. Our jaw movement also helps thin wax layers to fall off and cleans our ears. When you desire Ear wax removal Poole, always consult www.earwax.co.uk/ear-wax-removal-near-me/poole/
The middle ear contains the smallest bones of the body – the stapes, incus and the malleus. Together, these three bones are smaller than a penny!
One exposure to loud noises (85 decibels and higher) can permanently damage your ears. Hearing damage can occur within 7.5 minutes if you are exposed to 120 decibels.
Sound waves travelling in the air can travel up to 330 metres per seconds (m/s).

Even when you are asleep, your ears are listening. However, the brain has learned to ignore these sounds in order for you to sleep peacefully.
Eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the throat. This tube is responsible for the balance between body and atmospheric pressure. It is 5 inches in length and lined with mucous membrane.
The chorda tympani is a nerve that can influence your taste. The middle ear is a branch of a facial nerve that sends taste messages to your brain.
The skin of your ear grows about 1.3 inches per annum, so you get a new ear every 12 months as the old skin sheds.
